Sharks and rays live a lot longer than we thought
Evidence for systemic age underestimation in shark and ray ageing studies
Date: September 29, 2017
Source: James Cook University
- Summary: Sharks and rays live a lot longer than we thought — some twice as long as previously estimated.

Credit: © frantisek hojdysz / Fotolia
Many sharks are living much longer than was thought, according to a major review1 of studies on these important and often endangered top predators. This means that many estimates of how threatened particular species are — and decisions about whether they can be fished safely — could be based on faulty data.
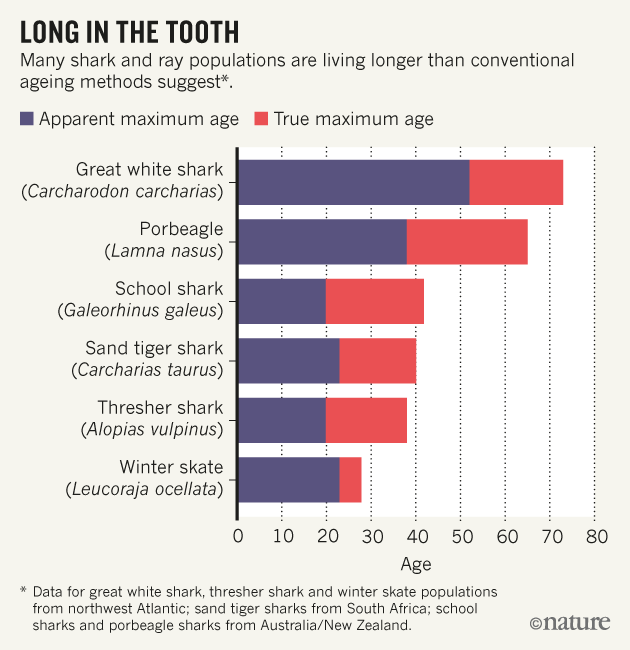
Scientists usually estimate how old sharks are by slicing through their spines and counting distinctive pairs of bands seen inside, which are often assumed to show age in the same way as the rings of a tree. But a growing number of cases are suggesting that the method can be problematic. For example, a 2014 study2 showed that sand tiger sharks (Carcharias taurus), which were thought to live for around two decades, can actually survive for up to twice that. And in 2007, researchers found3 that New Zealand porbeagle sharks (Lamna nasus) had been under-aged by an average of 22 years.
To investigate the scale of the problem, fisheries researcher Alastair Harry of James Cook University in Townsville, Australia, reviewed evidence for age underestimation. He reports in Fish and Fisheries1 that of 53 populations of sharks and rays for which there are good data, 30% have probably had their ages underestimated (see graphic). “Current evidence points to it being systemic, rather than restricted to a few isolated cases,” says Harry. “We really can’t ignore it anymore.”
Sharks aren’t trees
Growth rings are used to determine age in fish of all kinds. In teleosts (a group that contains the majority of bony fish), researchers tend to look at otoliths, lumps of calcium carbonate in the inner ear that build up layers regularly throughout the fish’s life. But sharks and rays don’t have otoliths, so researchers often use sections of vertebrae instead. Sometimes, when sharks stop growing, so do their vertebrae, which means that counting the rings can make an animal seem younger than it is.
Harry’s paper looked at two methods of checking whether the age estimated from counting rings is correct: chemical marking and bomb-carbon dating. In the former, researchers capture an animal and inject it with fluorescent dye that is taken up by its spine, making a permanent mark. When the animal is recaptured later, it is possible to count how many bands have formed since this known date. In the second method, scientists can look for carbon traces of 1950s nuclear-bomb tests in animals that were alive then, and use this to estimate age.
Harry has done “a very nice job”, says shark scientist Steven Campana of the University of Iceland in Reykjavik, who has worked on more than 100 ageing studies in sharks and rays, as well as in bony fish. “I fully agree with his conclusions: the shark age-underestimation problem is indeed a big one.”
Management headache
The study has wide-ranging implications, says Lisa Natanson, a fisheries biologist with the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in Narragansett, Rhode Island, who was one of the paper’s reviewers. If age information is wrong, models that guide fisheries’ decisions about how many animals can safely be caught will also be wrong.
Key processes such as growth, mortality and reproduction change with age, although precisely what this means for conservation will vary with each species. On the one hand, if living longer means that an animal matures and starts reproducing later in life, underestimating age will mean that it is more vulnerable than has been realized. On the other, living longer might give animals more breeding years, making a population more robust.
Emerging technologies could help to solve the ageing problem. Methods include looking at aspartic acid, an amino acid that is produced in living organisms in one of two forms, then slowly converts to the other in inert tissues through a process called racemization. Near-infrared spectroscopy could be useful too, says Natanson: “Complete reliance on backbones has got to disappear.”
- Nature
- 549,
- 316–317
- ()
- doi:10.1038/nature.2017.22626
